The Prosecution of Julian Assange Absolutely Threatens Freedom of the Press
2022-01-24 09:39
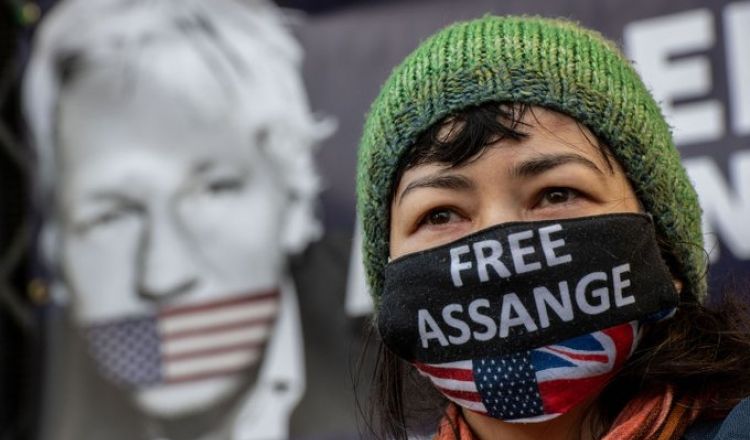

The Prosecution of Julian Assange Absolutely Threatens Freedom of the Press
By John Nichols-The Nation
The Biden administration should abandon a course that could lead to the criminalization of whistleblowers and investigative journalism
The Constitution does not prohibit assaults on freedom of the press because the notoriously vain founders were fond of the printers, who in the first years of the Republic produced what President George Washington decried as “diabolical…outrages on common decency.”
Washington’s thin-skinned successor, John Adams, had one printer arrested for allegedly libeling the president “in a manner tending to excite sedition and opposition to the laws.” Adams signed the Alien and Sedition Acts, which made it a crime to “write, print, utter or publish…malicious writing or writings against the government of the United States, or either house of the Congress of the United States, or the President of the United States.” He then had one of his leading critics, Matthew Lyon, tried and jailed after the representative from Vermont derided the second president’s “ridiculous pomp.” Lyon, it was charged, was “a malicious and seditious person, and of a depraved mind and a wicked and diabolical disposition.” Thomas Jefferson, no stranger to scandal, was similarly uncharitable. He deplored “the putrid state into which our newspapers have passed and the malignity, the vulgarity, and mendacious spirit of those who write for them.”
In other words, the founders rebuked the print publishers of their day with language every bit as venomous as that employed by contemporary US officials when they speak of Julian Assange, the WikiLeaks publisher whom the Biden administration proposes to try on espionage charges stemming from the 2010 publication of evidence of “Collateral Murder” atrocities committed by the US military in Iraq and Afghanistan. Assange attracts bipartisan acrimony. Senate minority leader Mitch McConnell has labeled him “a high-tech terrorist.” Former secretary of state Hillary Clinton, whose 2016 campaign was the target of WikiLeaks data dumps, has said, “The bottom line is [Assange] has to answer for what he has done, at least as it’s been charged.”
Last week, a court in the United Kingdom determined that Assange could be extradited to the United States to face prosecution by the Department of Justice for allegedly engaging in a hacking conspiracy with former Army intelligence analyst Chelsea Manning to reveal classified information.
To hear Assange’s prosecutors and critics tell it, his actions are indefensible. They would afford him no protection under the standards that are applied to preserve the ability of journalists to do their work—and publishers to distribute that work. Why? Because, we are told, even though WikiLeaks has been widely awarded and honored for producing journalism, Assange is “not a journalist.”
But, of course, the Bill of Rights makes no specific mention of journalists. The First Amendment speaks of “the press.” It was crafted in a time when printers distributed controversial, often incendiary screeds against the governing class. The publishers of the post-colonial era were rogues and rabble-rousers who spoke—or, to be more precise, printed—unwelcome truths to power. They knew full well that their publications provoked outrage. Benjamin Franklin, a printer who turned out to be one of the better of the founders, freely admitted as much when he concluded, “If all printers were determined not to print anything till they were sure it would offend nobody, there would be very little printed.”
The point of protecting press freedom has never been to privilege inoffensive speech, nor to establish a priestly class of journalists who are somehow deemed by the governing and economic elites to be acceptably employed. The point is to defend the free flow of information that the powerful would prefer to keep secret but that the people have a right to know. This is why Jefferson, on the eve of the 1800 election in which he upended Adams’s assault on press freedom, explained to Elbridge Gerry, “I am…for freedom of the press, and against all violations of the Constitution to silence by force and not by reason the complaints or criticisms, just or unjust, of our citizens against the conduct of their agents.”